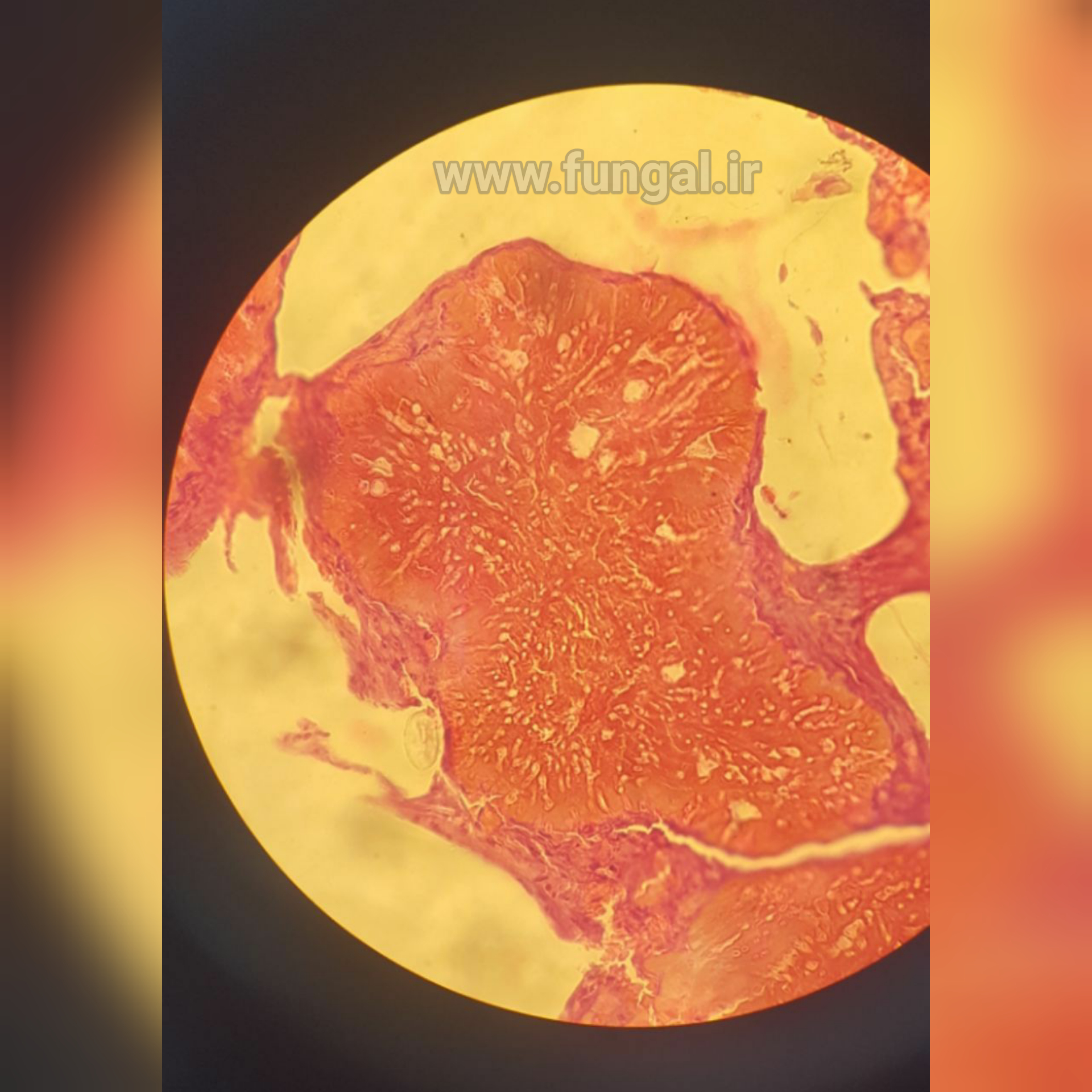
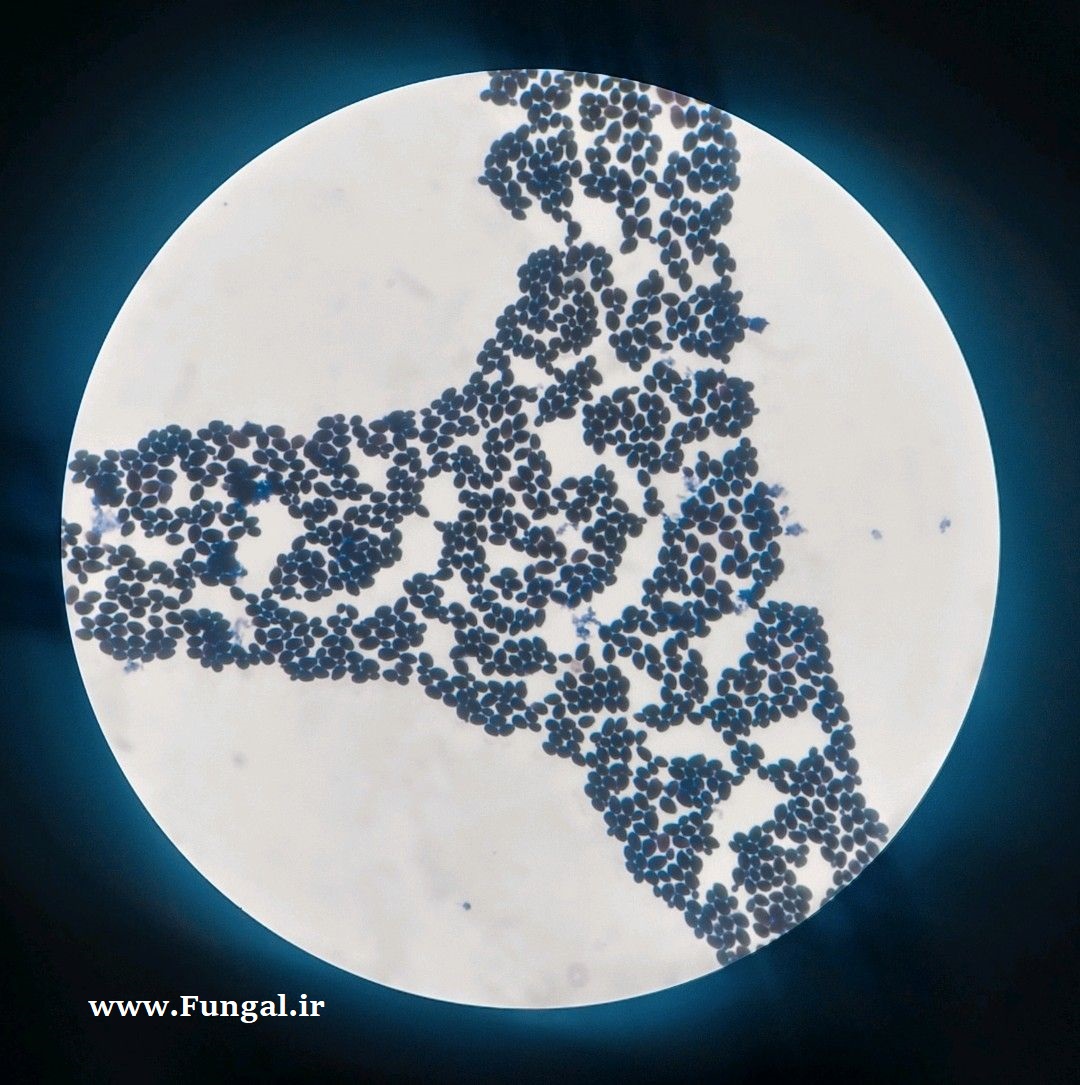
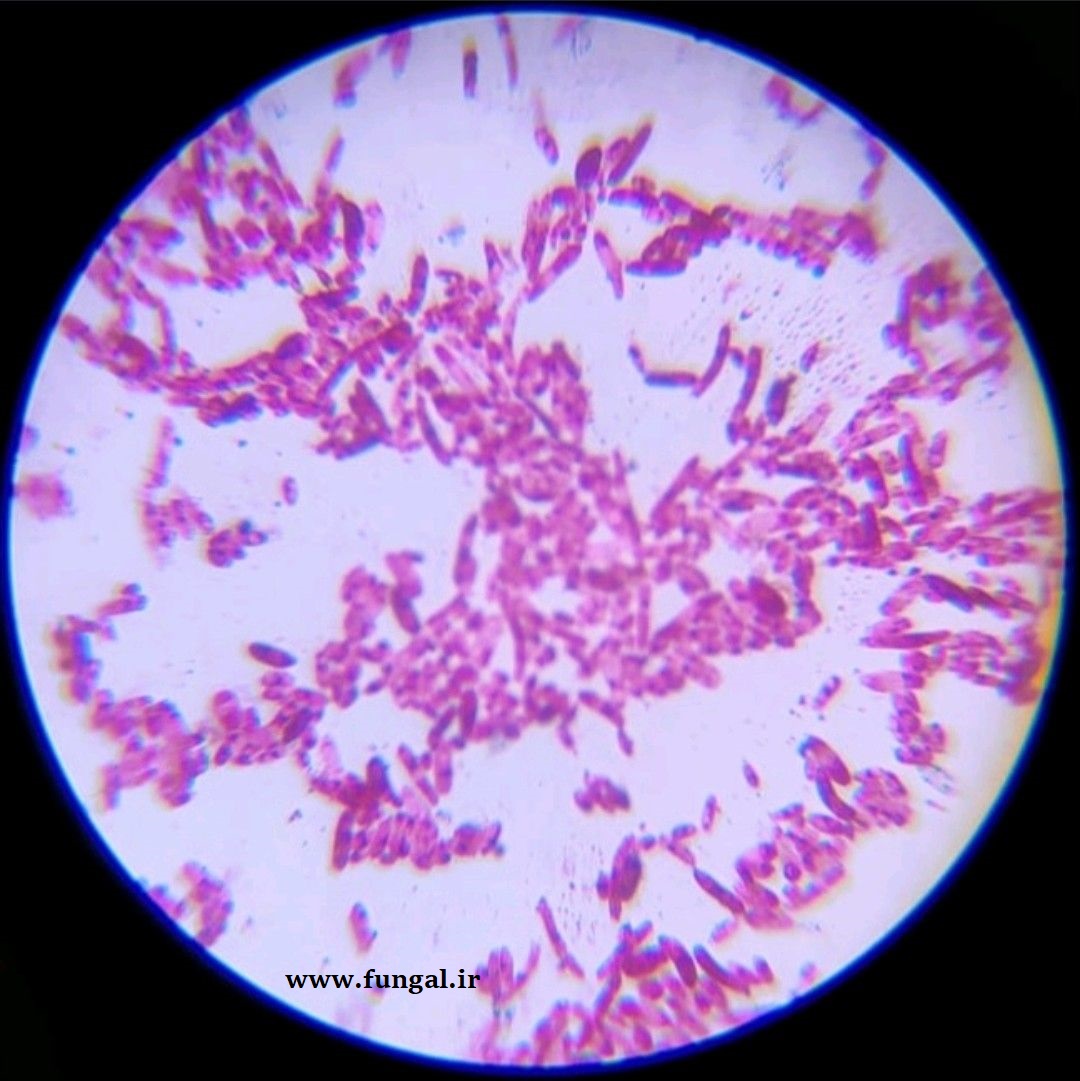
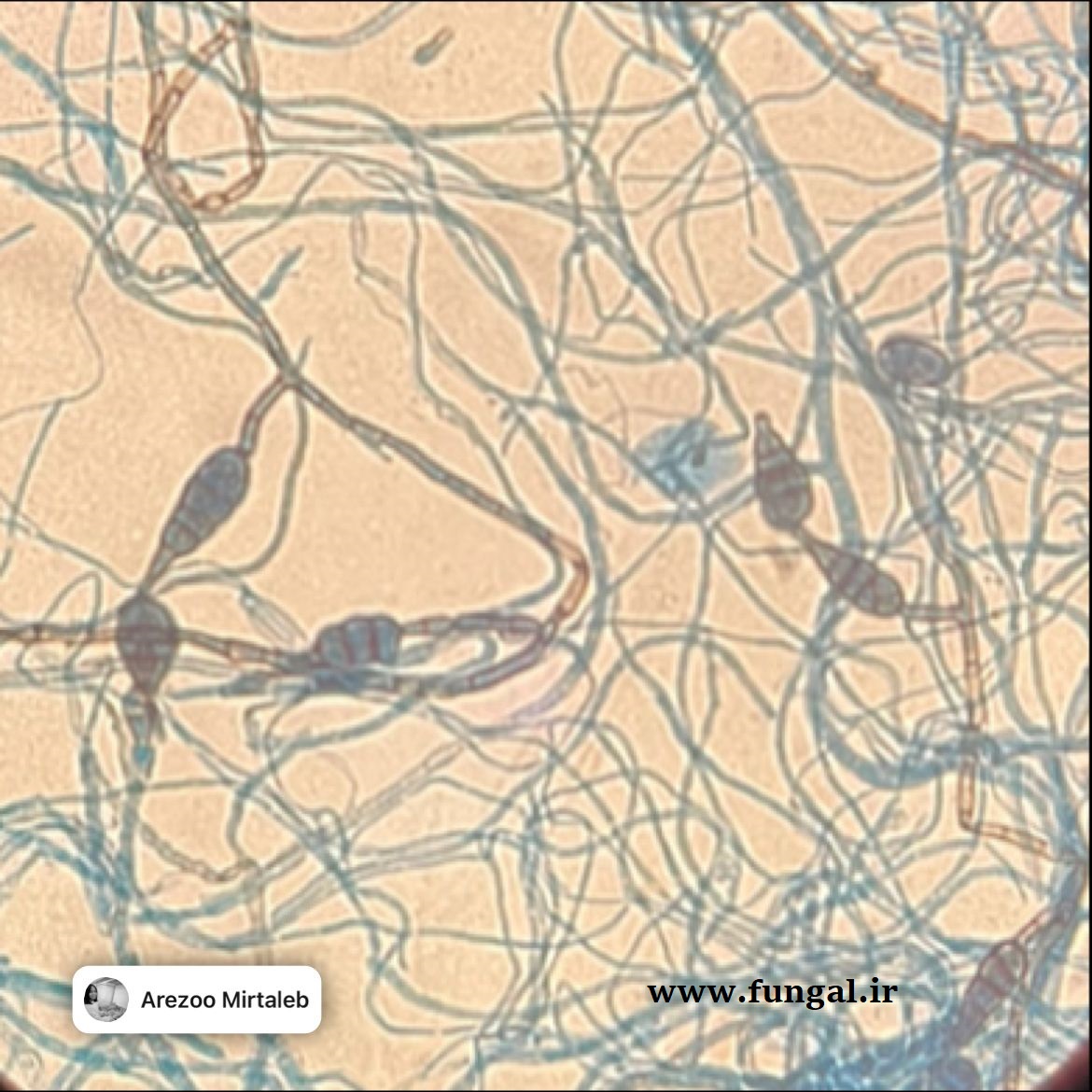
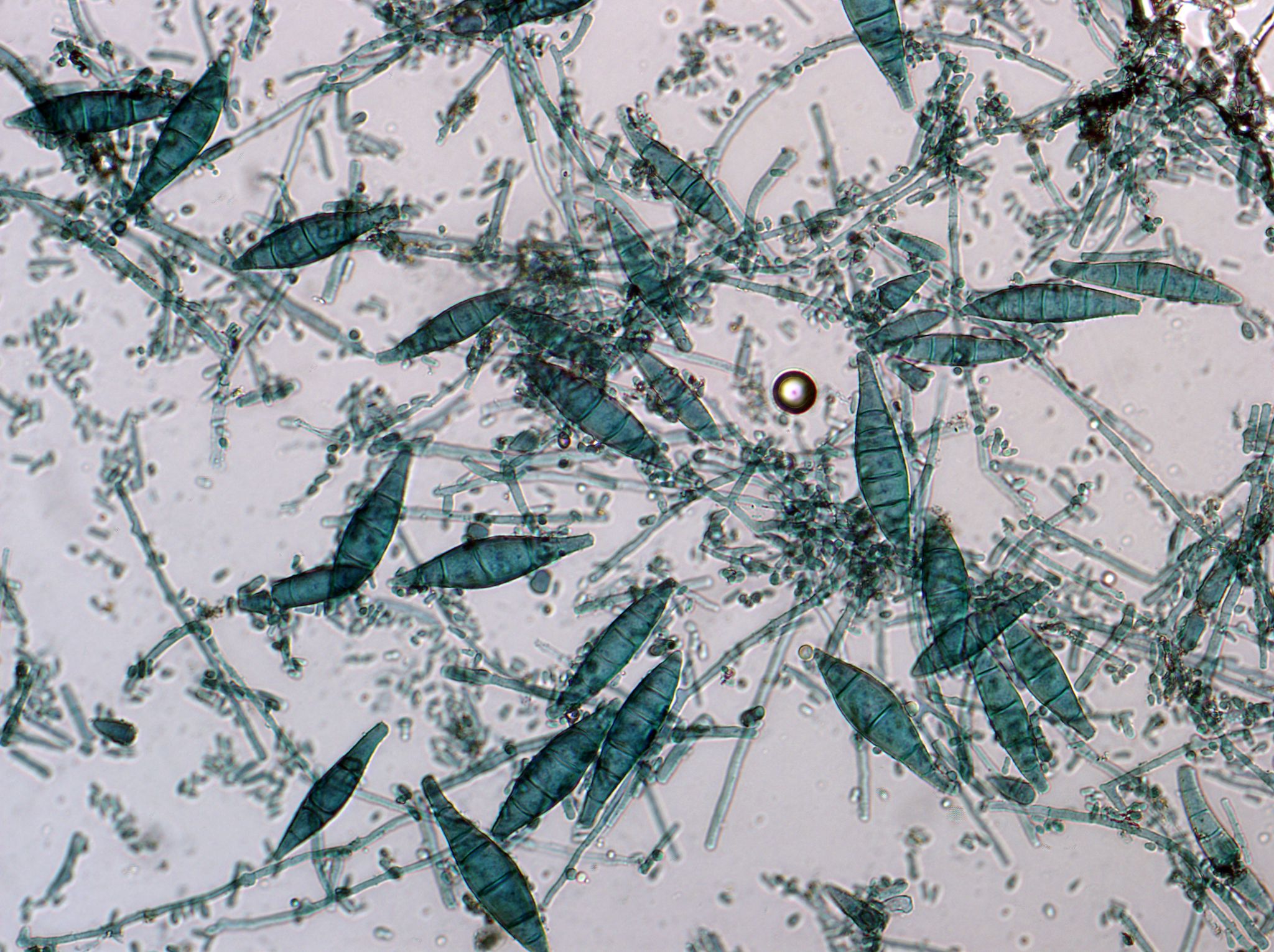
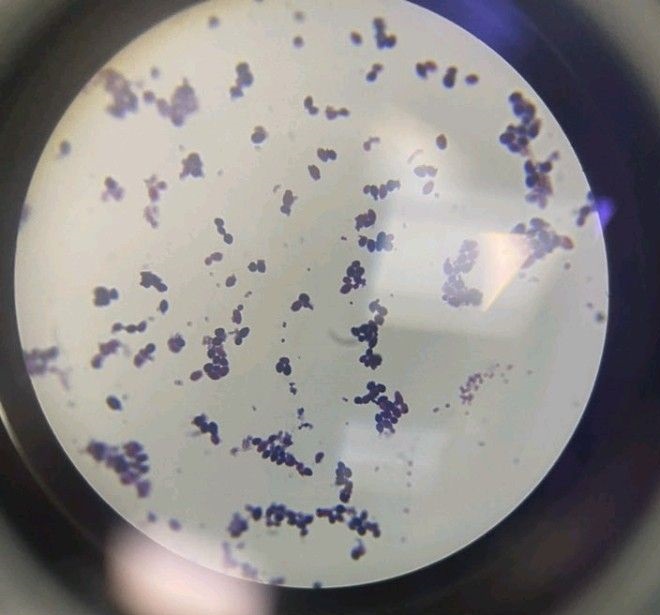
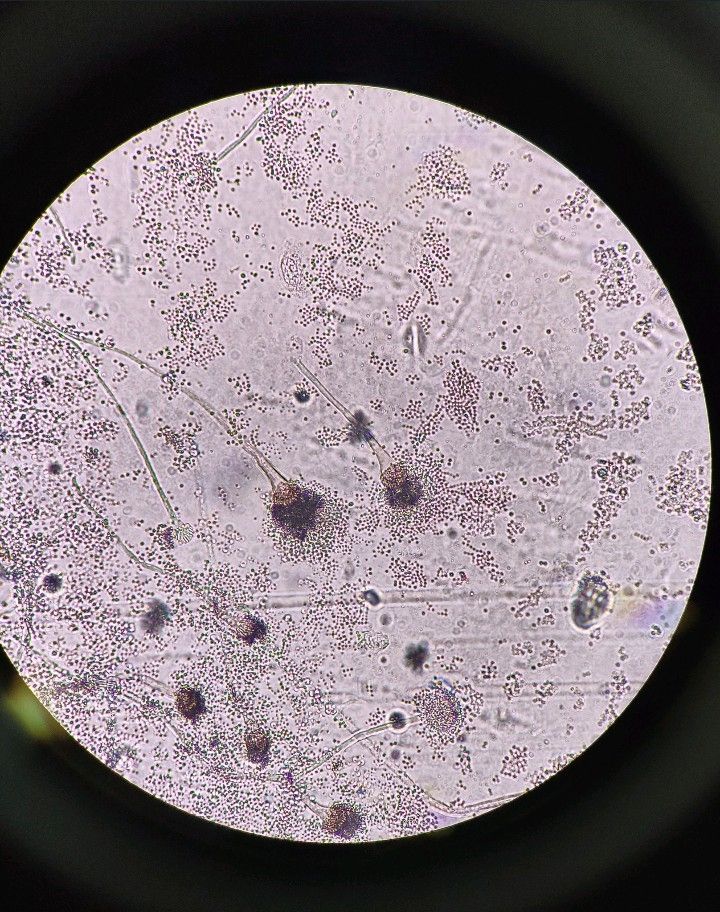
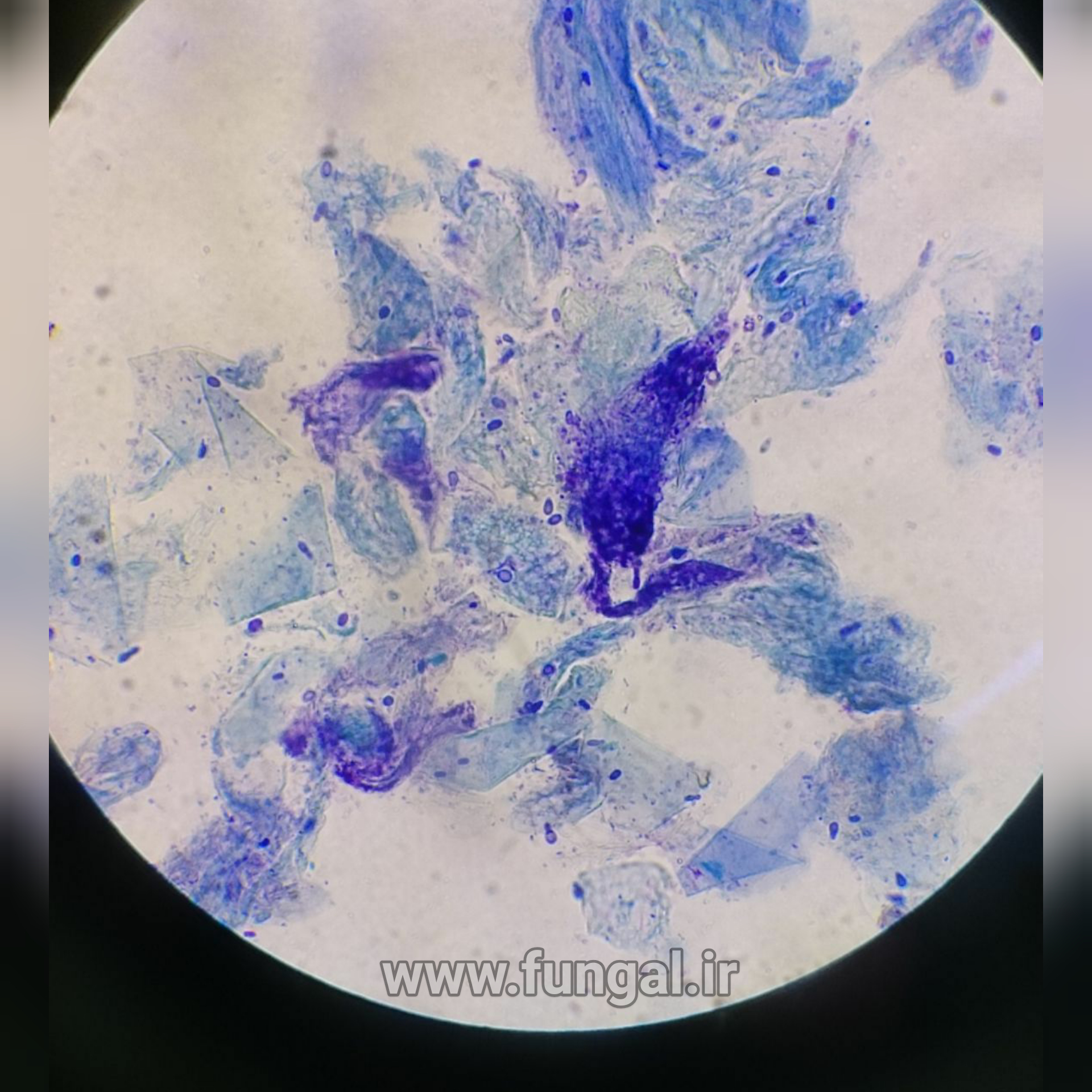
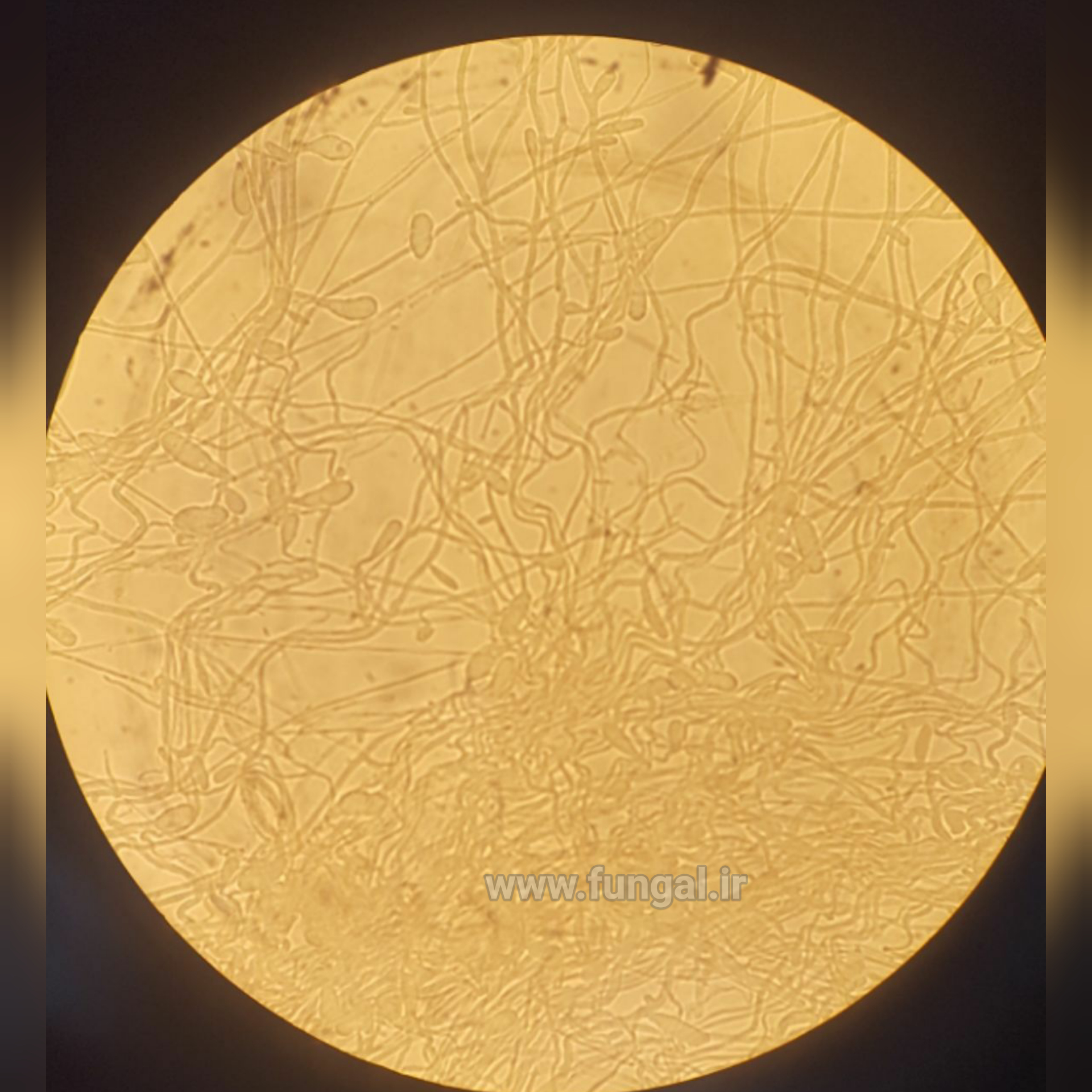
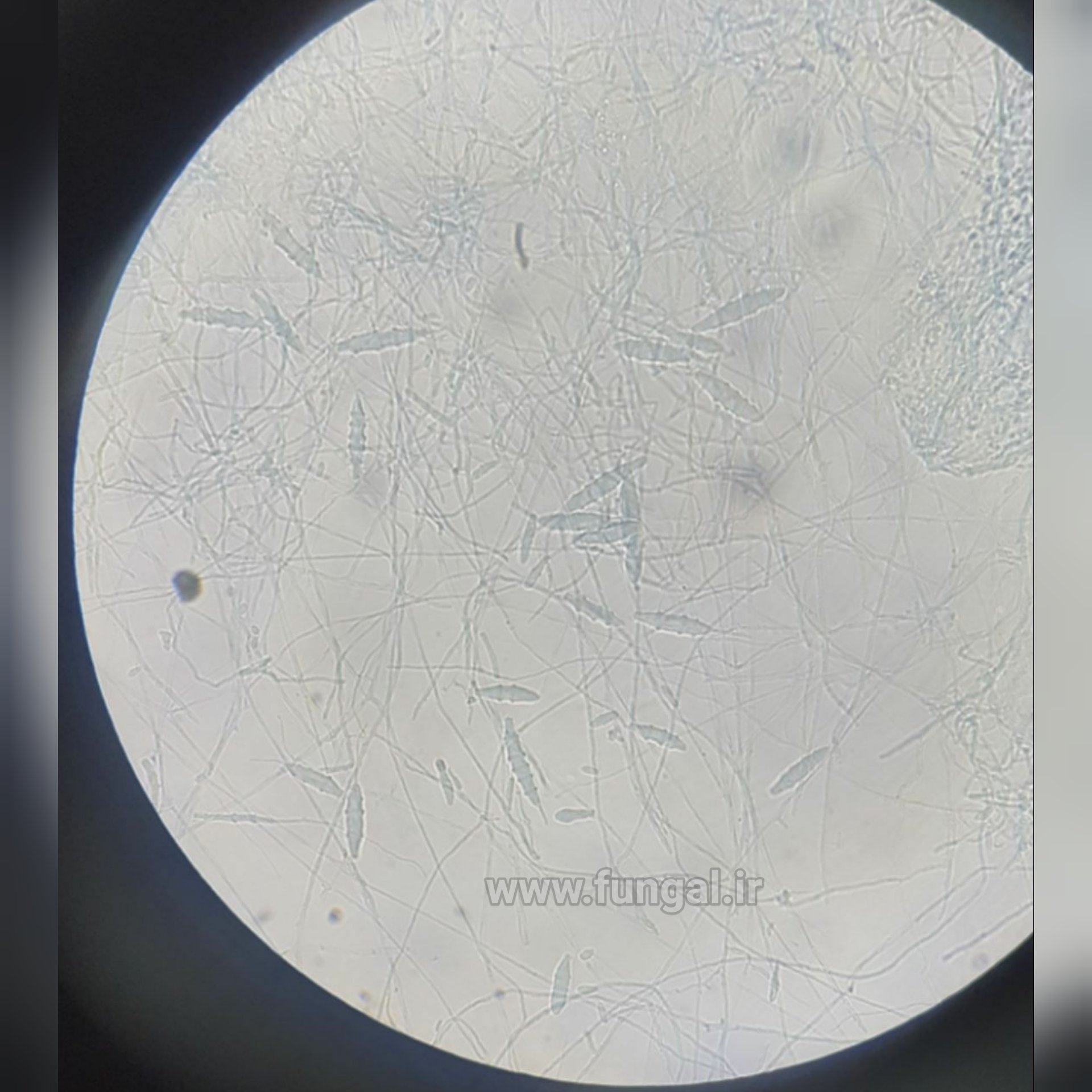
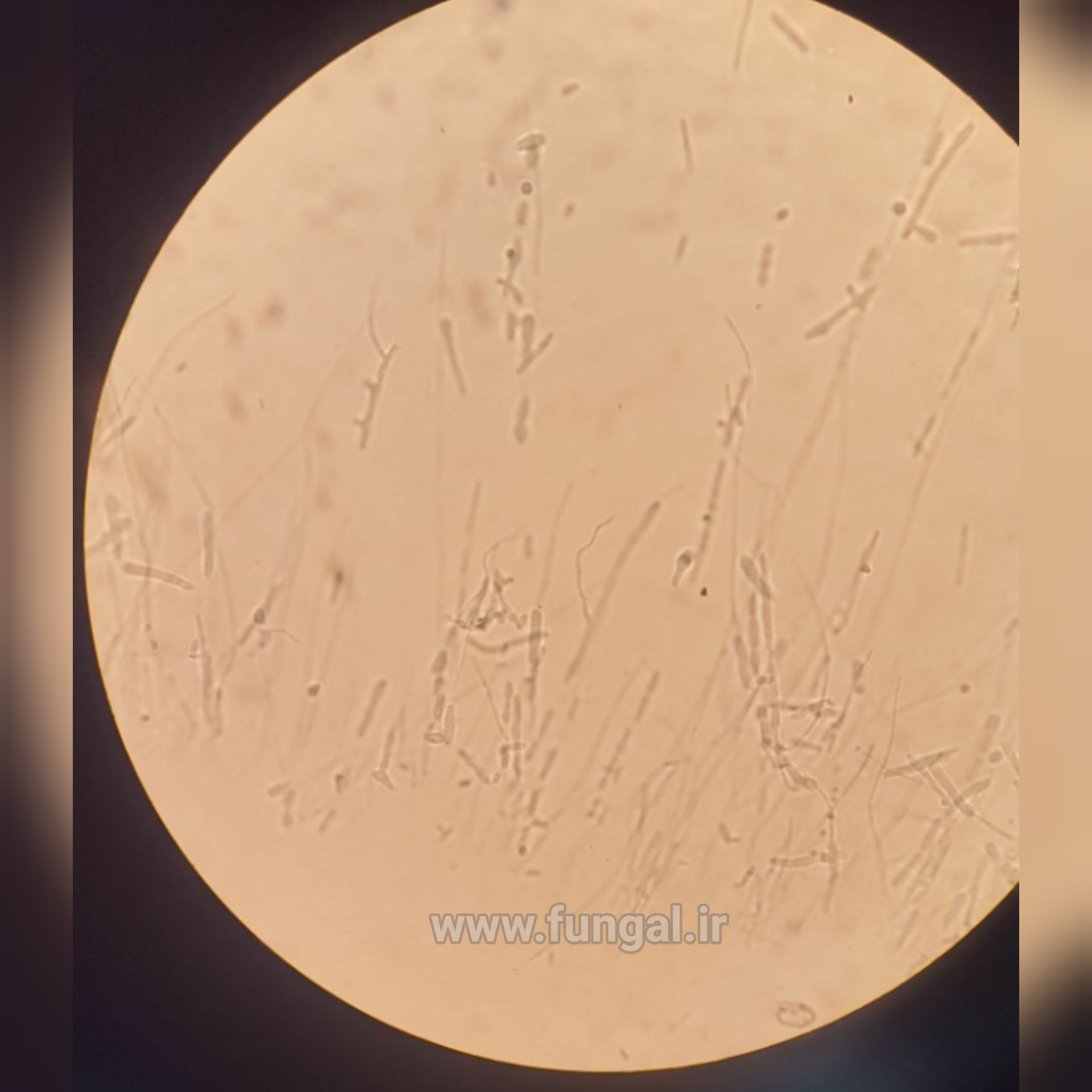
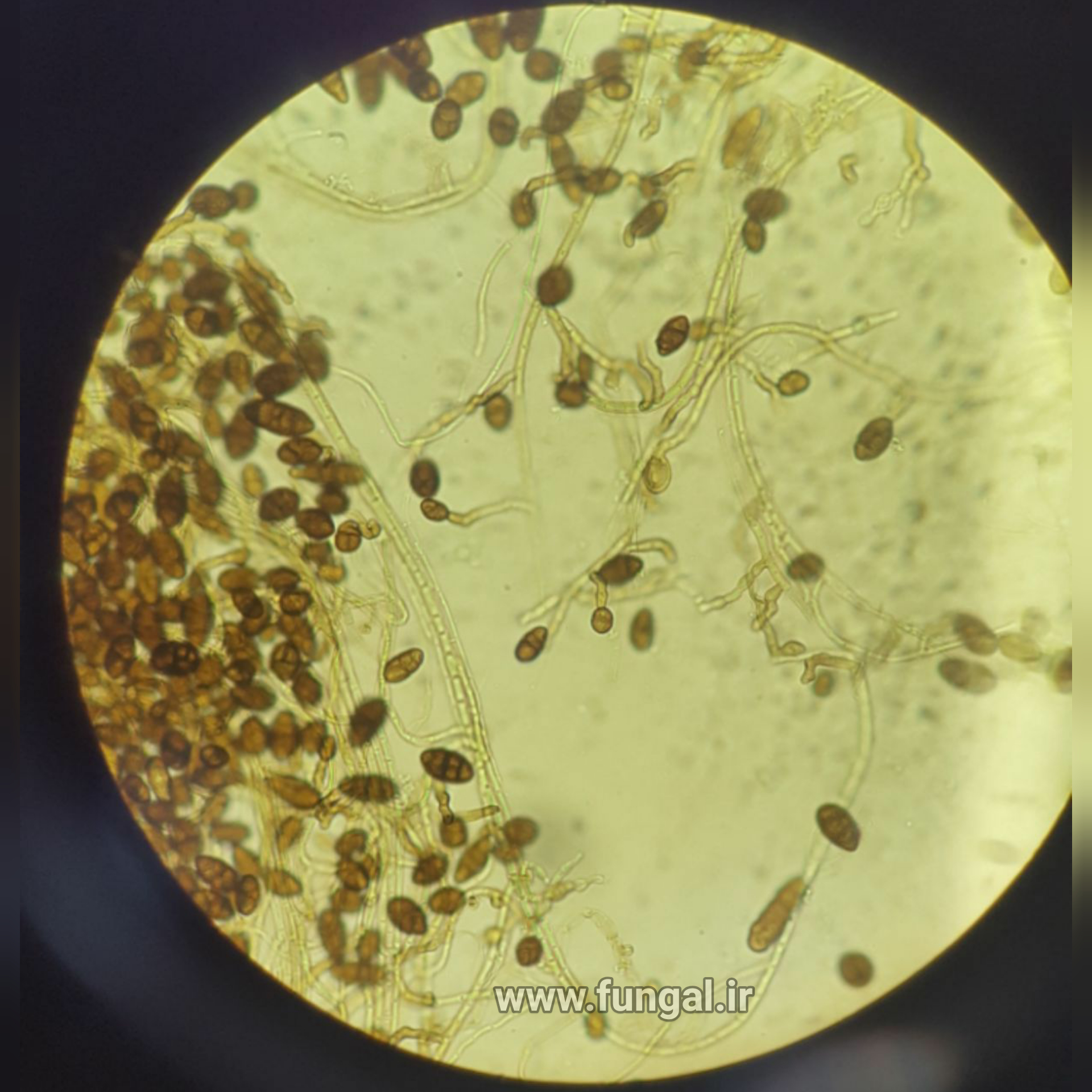
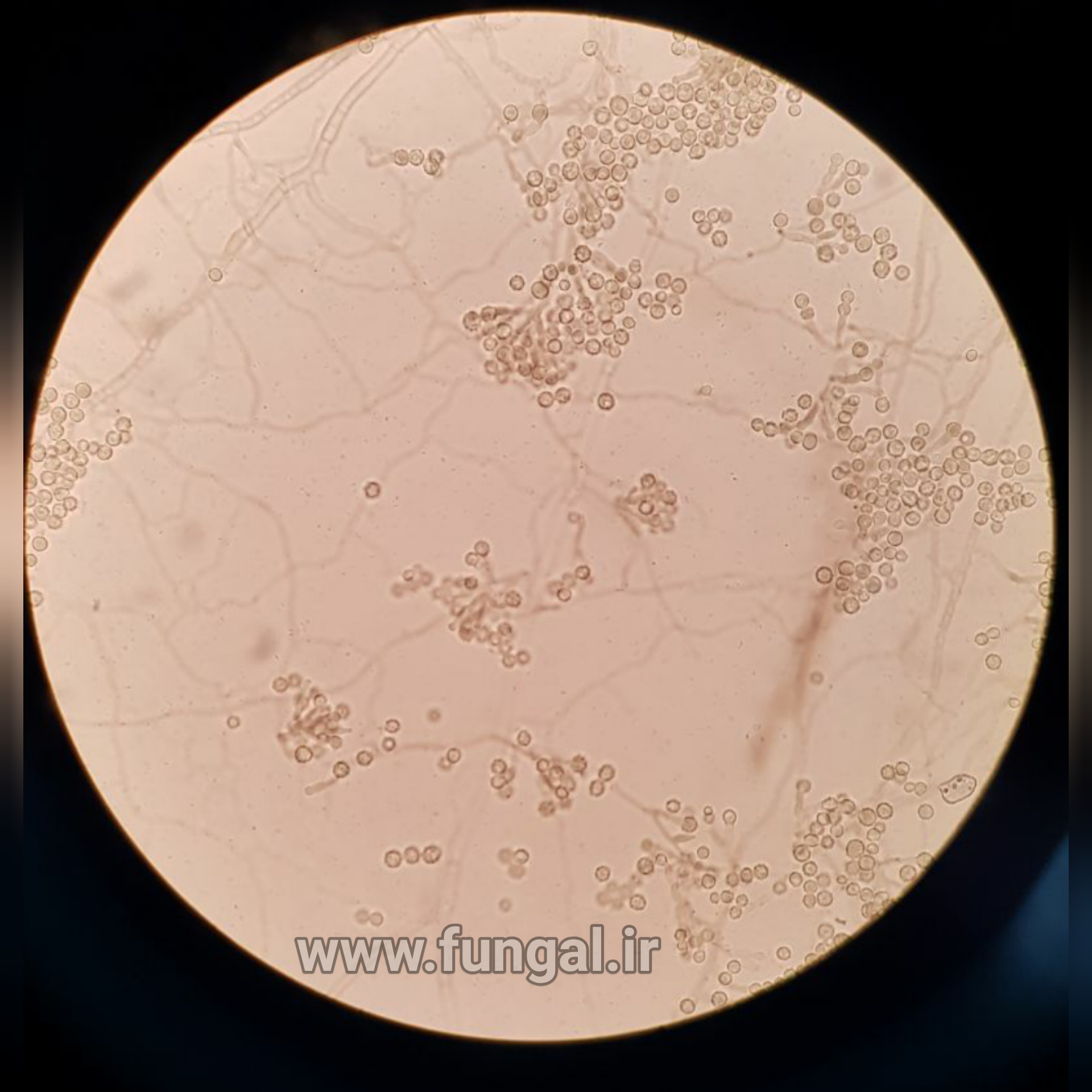
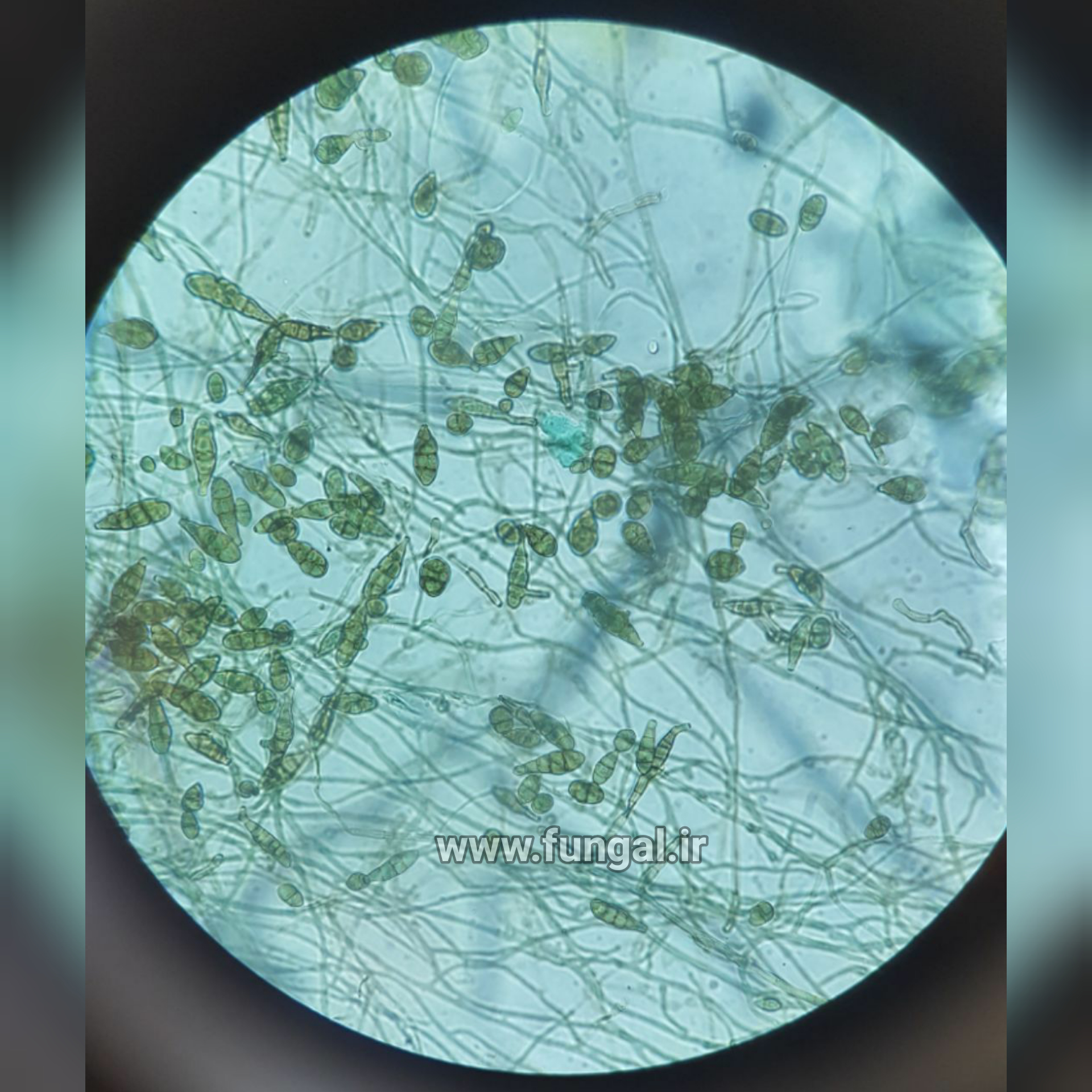
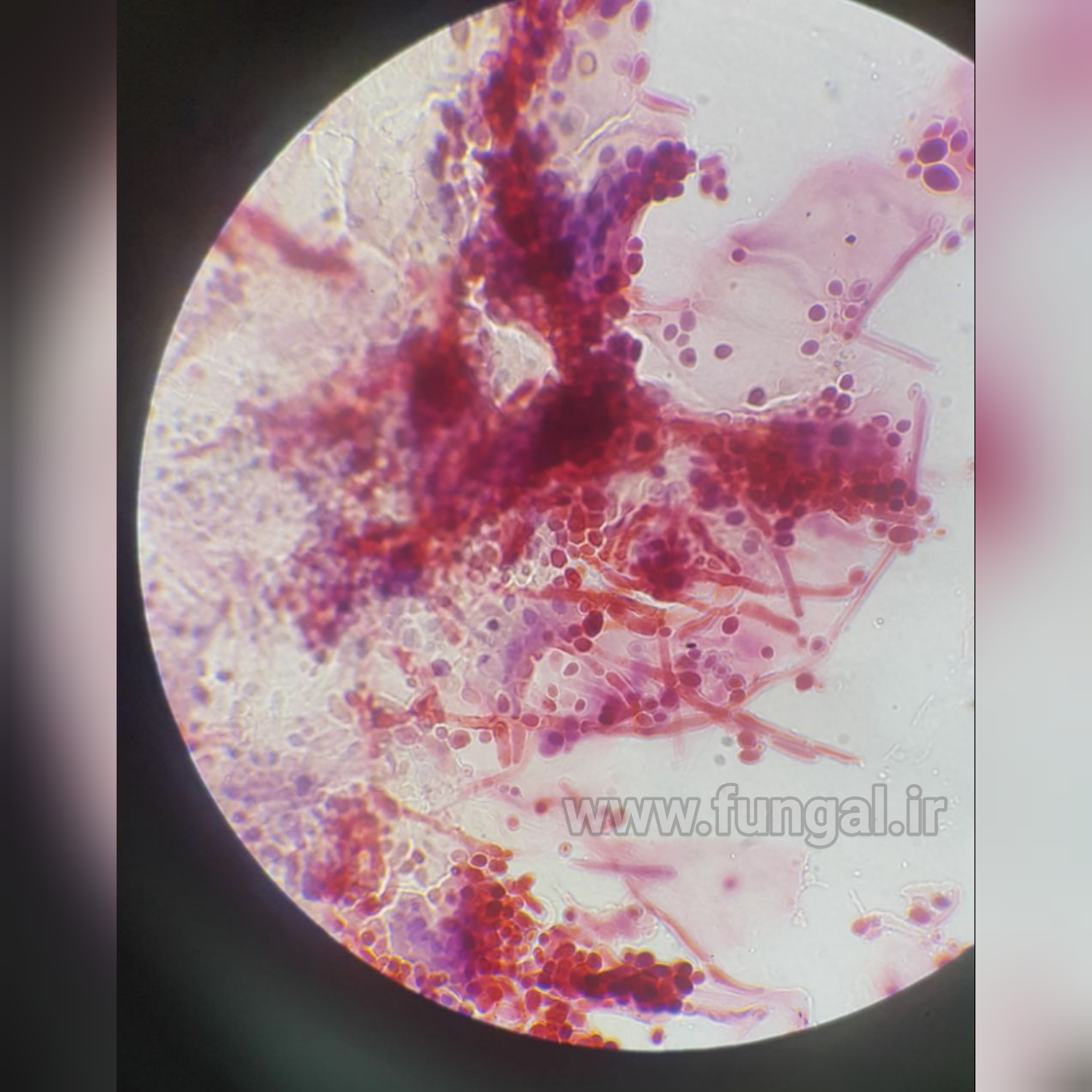
Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot, is a persistent fungal infection of the skin and the tissues just under the skin, affecting most commonly the feet, although it can occur in hands and other body parts. It starts as a painless wet nodule, which may be present for years before ulceration, swelling, grainy discharge and weeping from sinuses and fistulae, followed by bone deformity.
Several fungi can cause eumycetoma, including: Madurella mycetomatis, Madurella grisea, Leptosphaeria senegalensis, Curvularia lunata, Scedosporium apiospermum, Neotestudina rosatii, and Acremonium and Fusarium species.Diagnosis is by biopsy, visualising the fungi under the microscope and culture.Medical imaging may reveal extent of bone involvement.Other tests include ELISA, immunodiffusion, and DNA Barcoding.
Treatment includes surgical removal of affected tissue and antifungal medicines. After treatment, recurrence is common.Sometimes, amputation is required.
The infection occurs generally in the tropics, and is endemic in Africa, India and South America. In 2016, the World Health Organization recognised eumycetoma as a neglected tropical disease.